What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition that affects how the body uses blood sugar (glucose). Glucose is the main source of energy for the cells of the body and the brain. Your body can produce glucose on its own and get it from the foods you eat.
How it occurs?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that controls glucose levels in the blood and helps your body in the use and storage of glucose properly. Problem with the functioning and production of insulin causes high blood sugar levels known as hyperglycemia in medical terms which changes how your body handles carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. If you have diabetes your body does not produce enough insulin or any insulin and it interferes with the proper distribution of the glucose to reach your cells of the body, in other words, it’s a “traffic jam’’ in your bloodstream where glucose can’t flow efficiently.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes is often diagnosed in children and adults but can affect any age group. This type of diabetes is characterized as an autoimmune disorder in which your body’s immune system destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas resulting in a deficiency of insulin and high blood glucose level.
Prediabetes:
Prediabetes is a warning sign that you have a greater chance of developing type 2 diabetes. Adults with Prediabetes will have normal than high blood sugar levels but not high enough to be considered as diabetes and have no signs and symptoms. The normal blood glucose level falls between 70mg/dL to 90mg/dL. In patients with Prediabetes, the expected level of blood glucose can increase between 110mg/dL to 125mg/dL but do not meet the criteria to be classified as diabetes, due to which many people are not aware that they have Prediabetes.
Type 2 diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes is a common type of diabetes that mainly affects adults and can occur during childhood. In this type of diabetes, your body does not produce enough insulin and your body cells don’t use it effectively or don’t respond to it (insulin resistance).
Gestational diabetes:
The type of diabetes that occurs in some people during pregnancy is associated with mild or no symptoms, such as feeling unusual thirst or frequent urination. Hormonal changes during pregnancy sometimes play a role in gestational diabetes by making the body less able to use insulin. Gestational diabetes generally disappears after pregnancy. People with this type of diabetes are at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Why should you be aware of diabetes?
Diabetes is a serious public health problem and education about it to the community such as, what is diabetes, what causes it, and what increases your risk of developing diabetes are the key components that everyone should know, as it silently affects us without knowing us and many of us wake-up after a problem arises. Your awareness of these components will help in the early detection of diabetes, its prevention, prevention of associated complications, and the management of the disease.
Risk factors & symptoms:
Your chance of developing Type 1 diabetes is associated with
- Family history: Parents, siblings with Type 1 diabetes
- Age: any age, it frequently develops in children, teens, or young adults
- Genes and environmental factors such as viruses
Symptoms
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes can appear within a few weeks or months, nausea vomiting, and stomach pain similar to other health conditions. If you think you might have type 1 diabetes see your doctor and get a blood sugar test first.
Your likelihood of developing Prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes associated with the same risk factors
- Weight: Overweight or obesity
- Age: 45 or older
- Family history: Parents, siblings with Type 2 diabetes
- Physically inactive: Sedentary lifestyles
- Had diabetes during pregnancy
- Have Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Fat buildup in the liver
Symptoms
Prediabetes has no symptoms or mild symptoms which indicate the progress of Prediabetes to Type-2 diabetes, blurred vision, increased urination, and tiredness. Type 2 diabetes symptoms take several years to develop and are associated with, slow healing cuts, weight loss, feeling hunger than usual
You have a higher chance of developing gestational diabetes if you
- Had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- Have obesity or overweight
- Age more than 25
- Family history
- Have polycyclic ovary syndrome (PCOS) hormonal disorder
Symptoms: Gestational diabetes typically does not show any symptoms. It can be detected during the screening of blood sugar levels. However, some women develop symptoms if their blood sugar levels become too high, such as dry mouth, blurred eyesight, increased thirst, and itching in the genital area.
Prevention and management of diabetes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help in the prevention and your chance of developing diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes. Prevention is important if you are more likely to develop diabetes because of a family history or overweight.
Staying healthy with diabetes can be challenging. Living a healthy lifestyle helps a lot to keep your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels in ranges suggested by your healthcare provider. There are some steps that you need to take to prevent diabetes and for the management, if you have diabetes
- Weight Loss: One of the effective ways to reduce your risk of developing diabetes and the progression of the disease is to lose extra weight. Once you maintain your healthy weight it will improve your body better at using insulin which keeps blood sugar levels in check and also lowers chances of insulin resistance. To maintain a healthy weight you should set a target weight loss objective.
- Physical activity/exercises: Being physically active helps your body use insulin better and maintain blood sugar levels. There are many benefits of regular exercise, it burns calories and helps in controlling weight. Exercise lowers blood sugar levels and improves your body’s response to insulin. Some exercises help adults with weight loss
- Aerobic exercise: Such exercise includes brisk walking, swimming, biking or running. You should set a goal for 30 minutes of exercise from moderate to vigorous or 150 minutes a week.
- Resistance exercise: Such exercise includes yoga, weightlifting, pushups, and pull-ups. You should perform resistance exercises 2-3 times per week – to build strength, balance, and the ability to maintain an active life.
- Reduce inactivity: Cutting down on being inactive such as sitting at the computer can help control blood sugar levels. Take a few minutes to get up and move around after 30 minutes.
- If you have diabetes, weight loss & physical activity will help you in the management of disease by increasing the ability of your muscles to use more glucose for energy and lowering the blood sugar levels, it can decrease the need to use medicines, and also improve overall physical and mental health, increases energy levels, quality of life, and improve mood.
- Choose healthy plant-based food: Plants are a rich source of vitamins, carbohydrates, fibers, and minerals in your diet. Fiber-rich foods such as tomatoes, leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, legumes, beans, chickpeas, bread, whole grain rice, and whole oats help with weight loss and lower the risk of diabetes by
- Delaying the absorption of sugar and lowering blood sugar levels
- Helping you eat smaller portions because fiber-based foods are energy-rich
- Help in managing blood pressure
- Avoid bad carbohydrates: Avoid consuming foods that are high in sugars and less fiber or nutrients such as white bread,pasta from white flour, fruit juices, and pastries processed food with high sugar.
- Choose healthy fats: Fatty food with high calories should be eaten in small amounts. To maintain a healthy weight your diet should include food having good fats or unsaturated fats. Good fats include Olive, sunflower, cottonseed, canola oils, nuts and seeds, salmon fish, tuna, and cod help with weight loss and maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
- Make healthier choices: You can make your eating healthy by dived your plate in appropriate portions
- One quarter: whole grains
- One quarter: protein-rich foods
- One half: fruit and vegetables
- People with diabetes should choose a healthy meal plan that helps control blood sugar levels by providing regular balanced nutrition and preventing sudden increases in blood glucose levels. A healthy diet also supports overall health. Talk to your doctor or nutritionist to guide you in choosing a healthy diet plan according to your needs.
7. Take care of your mental health: Reducing stress helps in preventing and managing diabetes. Management of your stress will help you maintain your hormone levels which decrease the risk of insulin resistance. Feeling stressed, sad, and the development of anxiety can be common for people with diabetes. Ask for help from your health professional to learn healthy ways to lower your stress.
8. Check your blood glucose level at home if you have diabetes: if you have diabetes you should check your blood glucose levels at home to avoid high or low sugar levels whether you are taking insulin or diabetic medicines or not. It will help you and your health care to make changes in your diet plan, and physical activity, and make you able to understand how some types of food affect your blood glucose levels.
9. Use devices to manage diabetes: You can check your glucose level at home using a blood glucose meter. You have to prick your fingertip with a tiny needle that comes with a meter and put a blood drop on a glucose meter device, it will show a reading of how much glucose is in your blood at that moment.
- Continues glucose monitor: The device may benefit people who take insulin to manage their diabetes. The device uses a sensor in the tissue of your skin and shows changes in the blood glucose levels throughout the day and night and notifies you when your glucose level will be too high or low.
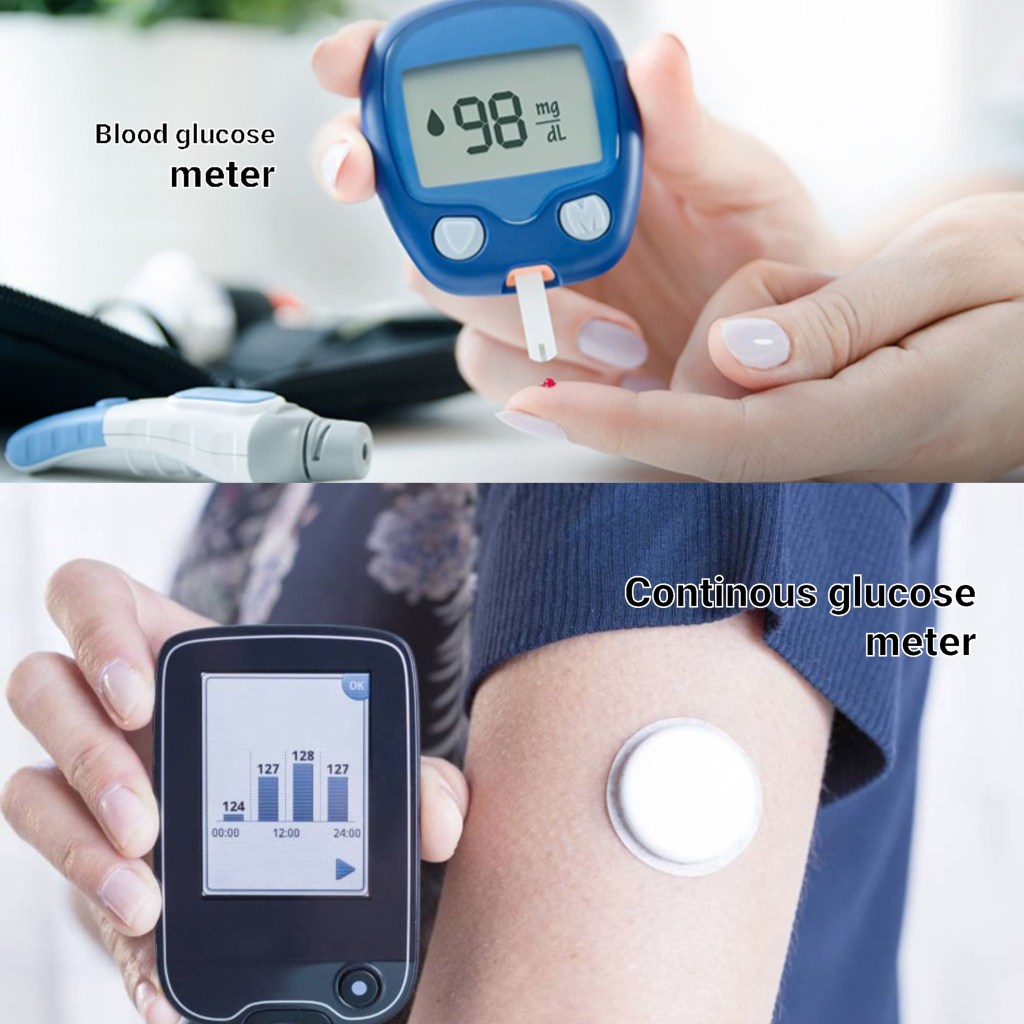
10. High and low blood glucose: People with diabetes should be aware of high and low blood sugar levels to manage their condition well.
- When your blood glucose level drops too low it’s called hypoglycemia. For most people glucose levels below 70mg/dL are considered too low and associated with feeling shaky, headache, and cold sweat. If you have experienced low blood glucose level you may need to change your diabetes meal plan activity and diabetic medicine by consulting with your healthcare as it can lead to fainting.
- When your blood glucose level is too high it’s called hyperglycemia. For most people glucose levels above 180mg/dL are considered too high and associated with feeling tired, and thirsty, urination too often, and having blurry vision
Conclusion: Understanding diabetes and how to handle it is important to prevent and manage diabetes and for staying healthy. By making good choices like, eating healthy, staying active and, keeping a healthy weight you can lower your chances of getting diabetes or manage it better if you already have it. Regular check-ups with your doctor can help you make sure you are doing well. Taking these steps leads to a healthier and happier life.
References
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes
Banday, M. Z., Sameer, A. S., & Nissar, S. (2020). Pathophysiology of diabetes: An overview. Avicenna journal of medicine, 10(04), 174-188.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/7104-diabetes
Knip, M., & Siljander, H. (2008). Autoimmune mechanisms in type 1 diabetes. Autoimmunity reviews, 7(7), 550-557.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459332/
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/type-2-diabetes
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/7104-diabetes
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/gestational
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/7104-diabetes
Deepa, M., Bhansali, A., Anjana, R. M., Pradeepa, R., Joshi, S. R., Joshi, P. P., … & Kaur, T. (2014). Knowledge and awareness of diabetes in urban and rural India: the Indian Council of Medical Research India diabetes study (phase I): Indian Council of Medical Research India diabetes 4. Indian journal of endocrinology and metabolism, 18(3), 379-385.
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/risk-factors/index.html
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/symptoms-causes
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/about/about-type-1
diabetes.html#:~:text=Currently%2C%20no%20one%20knows%20how,Managing%20your%20blood%20sugar.
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/signs-symptoms/index.html
https://www.healthline.com/health/type-2-diabetes/what-is-prediabetes#symptoms
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gestational-diabetes/
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/managing-diabetes